This article focuses on the concept of price,value and money and its relationship. Various questions can be framed in the economy section of UPSC IAS Prelims exams from this topic.
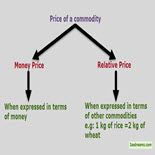
Price
1. It is the amount of money that needs to be paid in order to get one unit of a commodity.
2. It is the exchange value of the commodity where money is involved.
Example: Price of 1 kg of rice is 50 INR i.e. we need 50 INR of money in order to exchange rice(which is a commodity) of 1 kg.

General rise in Price level
1. Average price of many goods and services in an economy increases.
2. Occurs because of a rise in WPI or CPI and thus causes inflation.
Causes:
1. Excess demand of goods and services.
2. Deficit in supply of goods and services to compensate for the demand.
3. Higher cost of production because of high cost of raw material, tax, power, transport, etc. which may affect production in any way.
4. More purchasing power i.e. More supply of money in the economy as compared to the supply of goods and services.
5. Hoarding – a kind of speculative transaction where goods are purchased with the expectation that it will rise in the future.
General Fall in the Price Level
1. Average price of many goods and services in an economy decreases.
2. Occurs because of fall in WPI or CPI and thus causes deflation.
Causes
1. Excess supply of goods and services.
2. Fall in the demand of various goods and services including explorable items in foreign market.
3. Low purchasing power of people i.e. Less supply of money in the economy and lesser demand for consuming goods.
4. Falling trend in the business profit, employment, incomes, production of various goods and services as well as investment in both government and private enterprises.
Value

Value in Exchange
Ability to exchange commodity from one another.
Use Value
1. Importance given as per usage and need.
2. Low use value cause high marginal utility and vice versa.
[table id=9 /]
[table id=10 /]
Money
1. The exchange value for goods and services.
2. Paper notes/ currency are considered as legal tenders. ( Legal tender refers to the general acceptability of any medium of exchange as enforced by law)
Various forms of money supply in India
Rupees / Notes
Coins
Cheques
Debit and Credit Card, etc.
Function of Money
1. Acceptable medium of exchange for almost anything (for purchasing and selling).
2. Functions as a measure of value or a unit of a specific commodity.
3. Borrowing and lending can be easily done in terms of money i.e. it is standard of deferred payment.
4. Saving can be done through money i.e. money can be stored for future use.
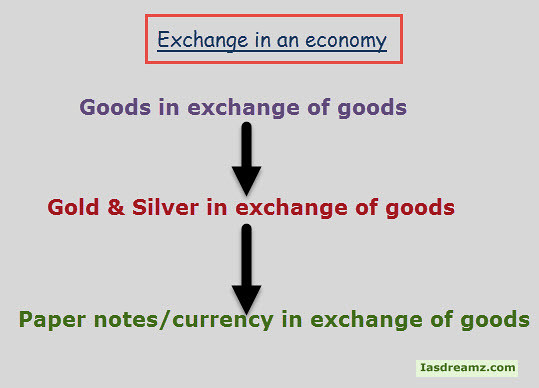
Difference between Barter Economy and Money Economy
[table id=11 /]